Protein For Weight Loss Female: How Much High-Protein Intake Helps You Lose Weight
Our Nutrition Assistant AI Suite will transform your body. You will lose fat, get toned, and build muscle. Gain confidence and optimal health.
You may feel stuck if your weight loss has slowed even after cutting calories. A high-protein diet can help by reducing hunger, protecting muscle, and supporting steady fat loss. Evidence suggests protein intake is a powerful tool for weight management when used with smart habits.
This guide explains how much protein for weight loss female goals usually requires, which foods are high in protein, and how to spread protein during the day. You will also find safe ways to raise your daily protein intake without adding unwanted calories.
Learn simple steps to get enough protein and move closer to your target weight. Keep reading for practical tips you can use today.
Key Takeaways
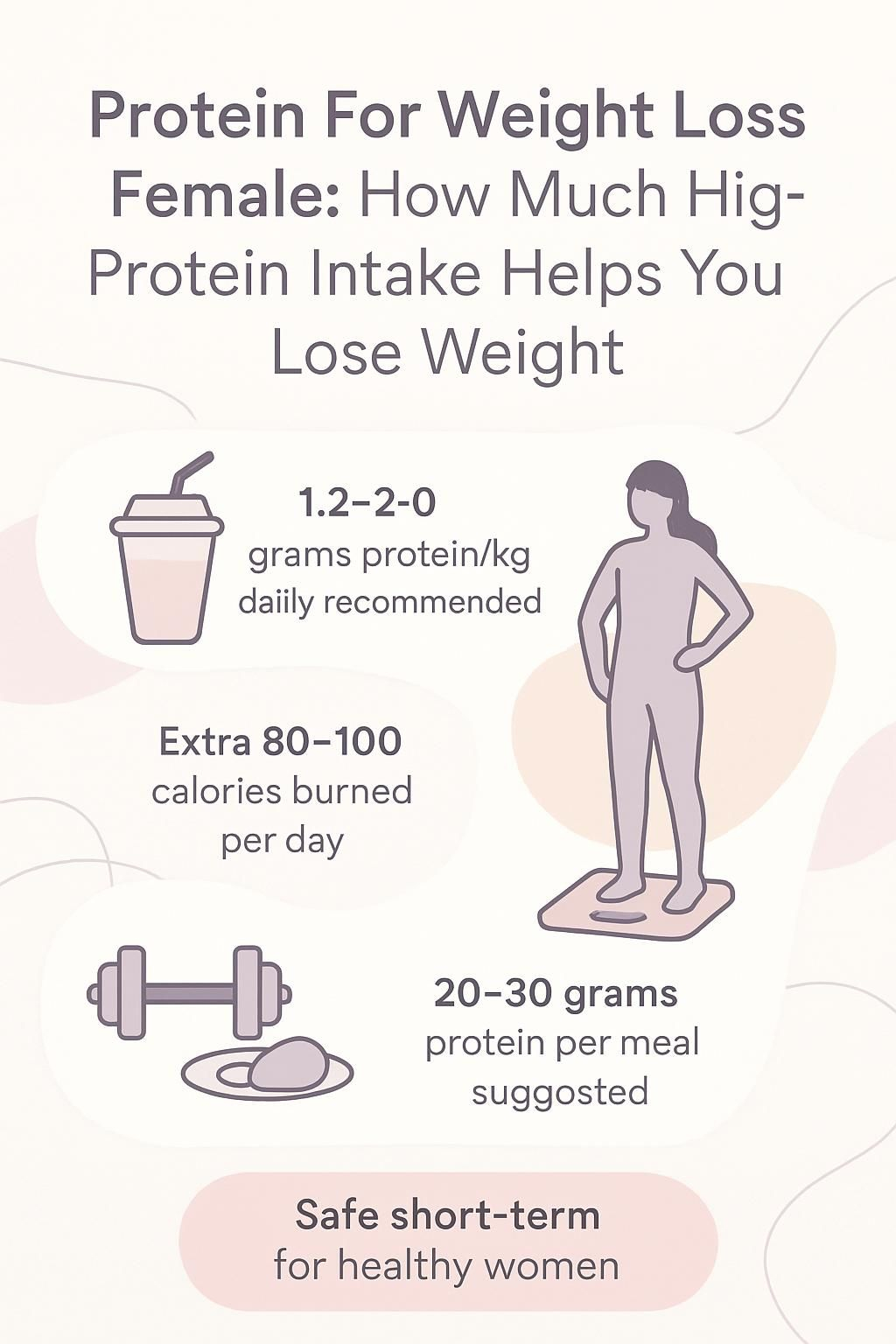
- Women who want to lose weight can aim for 1.2 to 2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight each day to protect muscle and cut fat.
- Higher protein intake raises fullness hormones like GLP-1 and PYY, lowers the hunger hormone ghrelin, and can increase calorie burn by about 80 to 100 calories daily.
- Clinical data supports 20 to 30 grams of protein per meal from lean meats, dairy, eggs, beans, or plant-based protein for best results.
- Short-term high protein intake is safe for most healthy women. Anyone with kidney disease should talk with a healthcare professional first.
- Mix animal and plant-based protein with fiber-rich foods to help steady blood sugar and support long-term weight management.
How Does Protein Support Weight Loss in Women?

Protein works on multiple fronts. It helps you feel full, guards your muscle during dieting, and supports a lower calorie intake without constant hunger.
How Does Protein Promote Satiety and Reduce Hunger?
Eating enough protein at each meal helps you stay full longer and curb cravings. Foods high in protein like eggs, lean meat, beans, and nuts raise satiety hormones such as GLP-1 and PYY while lowering ghrelin, the hunger hormone.
A large egg has about 6 grams of protein and can help keep cravings in check. Protein also has a higher thermic effect of food, which means your body uses more energy to digest it. That can add up to about 80 to 100 extra calories burned per day.
Spreading protein across four to five smaller meals or snacks can steady appetite. Whey protein supplements may further boost fullness signals like GLP-1 and GIP, which can make it easier to stick to a weight-loss diet.
How Does Protein Help Preserve Muscle Mass During Weight Loss?
During calorie restriction, your body may break down muscle for energy if protein intake is too low. High-protein diets supply essential amino acids, the building blocks your body uses to repair and build muscle instead of losing it.
Research supports 1.2 to 2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day to maintain or increase lean mass while cutting fat. If you weigh 70 kilograms, a daily target of 84 to 140 grams can fit these goals.
Slow-digesting casein, found in Greek yogurt and cottage cheese, releases amino acids gradually and can help overnight recovery. During one of my fat loss phases, raising protein at each meal and pairing it with strength training made workouts feel stronger and reduced fatigue.
How Does Protein Improve Body Composition?
Higher protein intake helps you build or keep lean muscle while losing body fat. Studies show adding supplemental protein, such as about 24 grams per day for eight weeks, can improve muscle mass and reduce fat.
Plant-based options like pea or soy protein also support better body composition. Protein-rich foods like dairy and eggs can shift your ratio of lean tissue to fat, often lowering body mass index.
Clinical trials find that getting enough high-quality, complete protein leads to greater benefits than low-fat diets alone. Hitting 20 to 30 grams of protein per meal can help your metabolism and body composition as you work to lose weight.
Protein fuels muscle repair and growth, which supports a leaner, stronger body while you lose fat.
How Does Protein Aid in Losing Weight?
Protein supports weight loss in two key ways. It increases the calories you burn from digestion and helps you keep lean body mass as you reduce calories.
How Does Protein Boost Metabolism?
Protein increases calorie burn because of the thermic effect of food. Your body uses about 20 to 30 percent of protein calories just to digest and process it, which is higher than carbohydrates or fat.
This boost can raise daily energy expenditure by about 80 to 100 calories. Some people notice a bigger lift when their total protein intake climbs over 100 grams per day. Whey protein isolate absorbs quickly and has been linked to greater satiety and extra fat loss in randomized trials.
A post-workout whey shake can help you feel fuller and support your resting energy burn during the day. Plant-based options like lentils also help maintain your metabolic rate during a calorie deficit.
How Does Protein Support Fat Loss While Maintaining Lean Mass?
Protein helps you lose more fat while keeping muscle. Studies, including those using rice protein for eight weeks, show reductions in total fat and belly fat with higher protein intake.
You preserve lean tissue when you eat extra protein during weight loss. Casein digests slowly and can support muscle over several hours, which aids steady fat burning while protecting strength.
Women who aim for 20 to 30 grams of protein per meal often report better muscle tone and energy as they lean down.
How Does Protein Regulate Appetite Hormones?
High-protein meals change hunger hormones in your favor. They lower ghrelin, the hormone that drives hunger, and raise GLP-1 and PYY, which signal fullness to your brain.
Whey protein can reinforce these effects by increasing GLP-1 and GIP. Many people notice fewer cravings for sweets or snacks once they hit their daily protein targets. Compared to carbs or fat, protein has a stronger impact on appetite control, which helps you stay consistent.
The next step is to learn how many grams per kilogram of body weight match your goals.
What Is the Recommended Protein Intake for Weight Loss?
Your protein needs depend on body size, goals, and daily activity. Use the guidelines below to get the right amount of protein a day for weight loss.
What Are the General Guidelines for Protein Consumption?
Aim for at least 20 to 30 grams of protein per meal to support satiety and energy balance. Spreading protein across four or five meals or snacks can help control hunger and steady blood sugar.
Choose both animal and plant-based proteins as part of a balanced diet. Focus on whole foods that are low in saturated fat and sodium to support heart health.
If you use a protein powder or a protein bar, replace existing calories rather than stacking extras. This helps you meet daily nutrient needs without unintended weight gain. High-protein diets are usually safe short-term for healthy adults. People with kidney disease should consult a healthcare professional before increasing protein.
How Do You Calculate Protein Needs Based on Body Weight?
First, convert your weight to kilograms. Multiply that number by 1.2 to 1.7 to estimate your protein range for weight loss and muscle maintenance. This range matches common recommendations for women who want to preserve lean mass while losing fat.
Example: at 70 kilograms, target 84 to 119 grams per day. Some women prefer a simple method like 30 grams of protein at each of three meals, with small snacks as needed. If you begin a new training plan, adjust your protein intake to match your activity and recovery needs.
If you have any medical conditions or take daily medicines, get guidance from a healthcare provider or registered dietitian before making large changes.
Best Protein Sources for Weight Loss
Choosing quality protein sources helps you meet goals with fewer calories. Here are practical options that are high in protein and easy to use.
Which Lean Animal Proteins Are Best?
Skinless chicken breast offers about 26 grams of protein in a 3-ounce serving and has little fat. Skinless turkey and lean cuts of beef such as loin or round provide around 22 grams per 3-ounce portion with lower saturated fat.
Fish is another strong choice. A 3-ounce fillet typically offers 17 to 20 grams of protein. Canned tuna packs about 39 grams per one cup serving and works well after a workout. One large egg adds about 6 grams.
For heart health, pick options with less than 10 grams of total fat and under 4.5 grams of saturated fat per 100 grams.
What Are the Top Plant-Based Protein Options?
Beans, lentils, tofu, and quinoa are reliable plant-based protein sources. A 3-ounce portion of firm tofu has about 9 grams. Half a cup of cooked lentils provides 9 grams and the same amount of kidney beans offers about 7 to 8 grams. One cup of cooked quinoa adds around 8 grams.
Nuts and seeds can raise your daily protein intake. One ounce of almonds delivers 6 grams. Two tablespoons of peanut butter provide about 7 grams and almond butter gives roughly 6 to 7 grams.
Pea protein is a complete plant option and may help with fullness through its effect on satiety hormones. Many people feel satisfied longer after meals built around these whole foods.
Which Dairy Products Are High in Protein?
Dairy can make it easier to reach your targets. A 6-ounce serving of Greek yogurt has about 17 grams of protein. One cup of cottage cheese offers around 23 grams; even a half cup provides more than 12 grams.
Cheese gives useful amounts in small portions. Many types provide about 7 grams per ounce. Low-fat yogurt offers about 6 grams in 4 ounces and low-fat milk provides roughly 8 grams per cup.
Adding Greek yogurt or cottage cheese to breakfast can keep you full through mid-morning without raising blood lipids when kept within daily needs.
What Protein Supplements Are Effective?
Whey protein contains all essential amino acids and absorbs fast. It can raise GLP-1 and GIP, which support fullness. Casein is also complete, but digests slowly, making it useful between meals or before sleep.
Soy protein is complete and contains isoflavones, which are antioxidants. Pea protein is a strong plant option for shakes or bars. Rice protein is lower in lysine, so pair it with pea protein for a complete profile. Hemp offers omega-3 and omega-6 fats, but is low in lysine and leucine, so combine it with other sources. Egg white powder is low in fat and carbs.
Bone broth has helpful nutrients; it is not a complete protein source, so use it with other proteins. You can find these supplements in major grocery stores or online retailers focused on sports nutrition.
Types of Protein and Their Benefits
Different types of protein support weight loss in slightly different ways. Matching the type of protein to your routine can make daily habits easier.
What Are the Benefits of Whey Protein?
Whey protein is complete, easy to digest, and convenient for busy days. Research links whey to greater satiety and more weight loss compared with some other proteins. Whey raises fullness hormones and supports a higher thermic effect of food.
During weight loss, whey helps preserve muscle, which protects your metabolism. A simple shake after exercise can help you hit a daily protein target without a full meal.
How Does Casein Protein Support Weight Loss?
Casein digests slowly, providing a steady flow of amino acids for several hours. This can increase satiety and reduce snacking, especially at night. Taking casein in the evening may support muscle repair during sleep and help limit muscle loss while dieting.
Studies show casein can support body composition changes similar to whey when total protein is adequate.
What Are Common Plant-Based Protein Options?
Soy protein is complete and offers extra antioxidants. Pea protein supports satiety and pairs well with rice protein for a full amino acid profile. Beans and lentils provide protein along with fiber, which can help control appetite.
Hemp seeds add healthy fats but are lower in lysine, so combine them with other proteins. Bone broth adds variety, though it is not complete; include other protein sources to meet daily needs.
How Can You Increase Protein Intake?
Small changes add up. Aim to include a source of protein at every meal and most snacks to support satiety and muscle.
How to Include Protein in Every Meal?
Breakfast ideas include eggs, which provide 6 grams each, or Greek yogurt, which offers about 17 grams in a 6-ounce serving. For lunch and dinner, add skinless chicken breast for about 26 grams in 3 ounces. Beans and tofu work well in bowls and salads. Half a cup of beans or 3 ounces of tofu each provides about 9 grams.
Boost meals with an ounce of almonds for 6 grams or include cottage cheese for more than 12 grams per half cup. A scoop of protein powder in smoothies or oatmeal can fill small gaps. Swapping some grains for quinoa adds about 8 grams per cooked cup.
Consistent protein intake supports muscle during weight loss and improves appetite control due to its higher digestion cost and hormone effects.
What Are Healthy High-Protein Snacks?
Good options include Greek yogurt, low-fat cottage cheese, hard-boiled eggs, nuts, and simple protein shakes. A 6-ounce serving of Greek yogurt has about 17 grams of protein. Half a cup of cottage cheese offers more than 12 grams. One large egg adds 6 grams and an ounce of almonds adds 6 grams.
Two tablespoons of peanut butter provide roughly 7 grams. If you need a fast option, mix whey, casein, or plant-based powder with water or milk for a quick snack.
How to Use Protein Powders in Smoothies and Recipes?
Add whey, soy, pea, or rice protein to a fruit smoothie for a simple high-protein meal. Stir a scoop into hot cereal or yogurt. Replace part of the flour in muffins or pancakes with casein or egg white powder to raise protein per serving.
Combine pea and rice proteins to get a complete amino acid profile if you prefer plant-based choices. Aim for at least 20 grams per serving to notice an effect on satiety and weight management.
Combining Protein with Other Nutrients for Weight Loss
Protein works best in balance. Pair it with quality carbs and healthy fats to keep energy stable and cravings low.
Why Is Balancing Carbs and Fats Important?
Carbs and fats are essential nutrients. Healthy fats from nuts, olive oil, fish, and avocado help you absorb fat-soluble vitamins and support fullness. Quality carbohydrates from fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, low-fat milk, or yogurt fuel daily activity and workouts.
You might try a simple target such as 30 grams of protein per meal, with room for healthy fats and high-fiber carbs. Too little fat can leave you tired, while too few carbs can make workouts harder. A balance of all three macronutrients supports better long-term results.
How Does Pairing Protein with Fiber Enhance Satiety?
Protein and fiber together slow digestion and steady blood sugar. This helps you feel full longer and reduces snacking between meals.
Practical ideas include a salad with grilled chicken and beans or eggs with black beans at breakfast. Aiming for about 30 grams of fiber per day with enough protein supports stable energy and fewer cravings.
Is a High-Protein Diet Safe for Women?
A high-protein diet is usually safe for healthy women. Monitoring is important if you have any medical conditions. Regular check-ins can help prevent problems.
Does High Protein Intake Affect Kidney Health?
People with kidney disease should be cautious with high protein intake because their kidneys may struggle to clear protein waste. For healthy adults, short-term intakes up to about 2.0 grams per kilogram of body weight per day are generally considered safe in research settings.
If you raise protein for the long term, get periodic lab tests to track kidney function and blood pressure. I once increased protein shakes during a training block and my doctor asked me to monitor labs; that helped me adjust to a level that felt good and kept markers in range.
Why Is Moderation and Variety Important?
Eating the same protein source all the time can raise health risks and miss key nutrients. Diets heavy in higher-fat animal proteins can raise saturated fat and cholesterol intake, which can affect heart health.
Use a mix of lean meats, dairy, legumes, and plant-based proteins. Diverse diets are linked to better long-term weight management and a lower risk of disease.
When Should You Consult a Healthcare Professional?
Talk to your doctor before starting a high-protein plan if you have kidney disease, diabetes, liver disease, or you take daily medicines. Protein can interact with some conditions and treatments.
A registered dietitian can help you calculate protein needs and design meals that match your goals. Seek help if you have ongoing digestive issues, headaches, or unusual fatigue after raising protein.
Common Myths About Protein and Weight Loss
Protein myths can slow progress. Clearing up these ideas helps you use protein intake more effectively to lose weight.
Does Eating Too Much Protein Cause Weight Gain?
Yes, if total calories go beyond what your body burns. Protein still contains calories. Overeating any macronutrient, including protein supplements or large portions of meat, can lead to weight gain.
Replace calories from refined carbs or added sugars with protein-rich foods instead of adding extra calories. Choose lean options to limit saturated fat.
Are All Protein Sources the Same?
No. Animal proteins like chicken and fish provide all nine essential amino acids in one food. Many plant sources are incomplete on their own, so combine them, such as beans with rice, to create a complete protein profile.
Whey absorbs quickly and suits post-workout recovery. Casein digests slowly and fits evening use. Some processed meats can be high in saturated fat and sodium, so choose leaner options more often.
Is Protein Only for Athletes and Bodybuilders?
Protein is for everyone. Your body needs it to maintain muscle, support metabolism, and control hunger. Studies show women who raise daily protein often lose more fat while keeping muscle compared with lower-protein diets.
Many experts suggest 1.2 to 2.0 grams per kilogram of body weight for women trying to lose weight while preserving lean mass.
Benefits of High-Protein Diets for Women
High-protein diets can help you eat fewer calories, burn more energy, and keep muscle while you lean down.
How Does Protein Reduce Calorie Intake?
Protein boosts fullness hormones and reduces hunger hormones, which can lower daily calorie intake. A higher-protein breakfast often leads to fewer calories later in the day.
Spreading protein across four to five eating times helps limit mindless snacking. The thermic effect of protein also burns about 80 to 100 extra calories as your body digests it.
How Does Protein Enhance Fat Burning?
Higher protein intake can raise your metabolic rate. For some women, moving from 15 percent to 30 percent of calories from protein can increase daily energy burn due to higher digestion costs.
Protein also protects muscle. Muscle burns more calories than fat, helping you maintain a healthy metabolism during weight loss.
How Does Protein Improve Muscle Tone and Strength?
Protein repairs exercise-induced muscle damage and supports growth. With steady resistance training plus enough protein, you will likely see stronger, firmer muscles over time.
Simple habits, such as adding eggs at breakfast or yogurt after workouts, can speed recovery and reduce soreness.
High-Protein Meal Ideas for Weight Loss
These simple meals help you reach your daily protein needs while keeping calories in check.
What Are Healthy High-Protein Breakfast Options?
Scrambled eggs or a veggie omelet provide about 6 grams of protein per egg. Add fruit or whole-grain toast for balanced energy. Greek yogurt, 15 to 20 grams per serving, pairs well with berries or nuts.
Cottage cheese offers roughly 13 grams per half cup and tastes great with sliced peaches or berries. If you like nut butter, spread almond butter on whole-grain bread for protein and healthy fats.
What Are High-Protein Lunch Ideas?
Grilled chicken salad with leafy greens and a light vinaigrette gives lean protein with fiber. Black bean quinoa bowls add plant protein and help keep you full.
Tuna or salmon wraps in whole grain tortillas provide protein and omega-3 fats. Quick options include cottage cheese with sliced veggies or hard-boiled eggs over spinach.
What Are Nutritious High-Protein Dinner Choices?
Skinless chicken breast with roasted vegetables is filling and high in protein. Try grilled fish like salmon or cod, about 22 grams in a 3-ounce serving. Beans or lentils offer around 18 grams per cooked cup and make great plant-based dinners. Tofu stir-fry with broccoli supports muscle repair.
Low-fat cottage cheese has more than 25 grams per cup and pairs with avocado or chickpeas for a simple, balanced plate. Combining beans with lean meats can help you reach daily targets.
What Are Good High-Protein Snacks?
Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, cooked lentils, firm tofu, nuts, and sliced cooked chicken all work between meals. Greek yogurt provides about 17 grams per cup and cottage cheese adds roughly 14 grams per half cup. Firm tofu provides about 10 grams per half cup.
Nut butter on whole-grain toast delivers staying power with 6 to 8 grams per serving. Preparing snack boxes with these foods can help you avoid high-sugar treats during busy days.
Success Stories: Women and Protein-Focused Weight Loss
What Are Real-Life Examples of Effective High-Protein Diets?
Many women do well with a plan that sets protein at about 30 percent of calories, along with vegetables and whole grains. Others follow a structure centered on lean meats, fish, eggs, and legumes at each meal.
A sample day might include Greek yogurt at breakfast, grilled chicken salad for lunch, and salmon with vegetables at dinner. Snacks could be boiled eggs or low-fat string cheese. Keeping protein consistent at each meal helps manage hunger and prevents overeating later.
Important Considerations for a Protein-Rich Diet
A protein-rich diet helps with satiety and muscle support. A few simple practices can make it safer and more sustainable.
Why Is Adequate Hydration Important?
Water helps your kidneys process protein waste and supports fat burning. Without enough fluids, you may feel sluggish or get headaches as your body adjusts.
Hydration also helps deliver nutrients to muscles and may curb false hunger. Carrying a reusable bottle is a simple way to keep intake steady throughout the day.
How to Avoid Overly Processed Protein Products?
Read ingredient lists and choose simple foods. Pick lean meats, eggs, fish, beans, and plain Greek yogurt instead of flavored or highly processed products.
Many bars and powders contain added sugars and artificial flavors. Cooking basic proteins at home, such as baked chicken or lentils, keeps meals nutritious and predictable.
Conclusion
Eating enough protein can change your weight loss journey. A high-protein diet helps you feel full, protects lean muscle, and may raise metabolism. For many women trying to lose weight, a mix of lean meats, beans, low-fat dairy, eggs, and nuts works well.
Increase your protein intake gradually over a week to reduce digestive discomfort. Pair higher protein with regular exercise and balanced carbs and fats for steady progress. If you have kidney disease, diabetes, liver problems, or take daily medicines, seek medical advice before making big changes.
Choosing quality protein sources and spreading protein throughout the day can support long-term weight management. Small, consistent steps add up to lasting results.
References: [1] U.S. Dietary Guidelines, protein and healthy eating patterns, dietaryguidelines.gov. [2] Leidy et al., The role of protein in weight loss and maintenance, American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. [3] Wycherley et al., High-protein diets and body composition, Nutrition & Dietetics. [4] Paddon-Jones et al., Protein distribution and muscle health, Journal of Nutrition. [5] Halton and Hu, Protein and satiety, Journal of the American College of Nutrition.
FAQs
1. How much protein should women eat for weight loss?
Most studies suggest that women aiming to lose weight benefit from eating 1.2 to 1.6 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight each day. For a woman weighing 150 pounds, this equals about 82 to 109 grams daily. Research published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition supports these numbers.
2. Does high-protein intake help burn more fat during weight loss?
Yes, higher protein intake helps preserve lean muscle while losing fat mass. A review in Obesity Facts found that diets with increased protein led to greater reductions in body fat compared to lower-protein diets.
3. What are good sources of high-quality protein for women trying to lose weight?
Lean meats like chicken breast and turkey, fish such as salmon or tuna, eggs, Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, tofu, lentils, and beans all provide quality protein with fewer calories from fat or sugar.
4. Can increasing dietary protein reduce hunger during a calorie deficit?
Eating more dietary protein can help control appetite by making you feel full longer after meals; several clinical trials show participants who ate higher-protein meals reported less hunger throughout the day than those on standard diets.
Summary: Women seeking effective weight management may see better results when they increase their daily intake of quality proteins within recommended ranges; evidence shows this approach preserves muscle mass and reduces hunger while supporting healthy fat loss goals. My own experience mirrors these findings—I felt fuller between meals and noticed improved energy levels after raising my daily lean meat and dairy servings within suggested limits.