Lose Fat Gain Muscle: Effective Tips For Body Recomposition
Our Nutrition Assistant AI Suite will transform your body. You will lose fat, get toned, and build muscle. Gain confidence and optimal health.
Losing fat and gaining muscle at the same time feels tricky. The good news is that body recomposition is possible when you align training, diet, and recovery. Research-backed methods help you lose fat and gain muscle without guesswork.
This guide walks you through practical steps for nutrition, resistance training, calorie targets, and tracking. You will see what truly moves the needle for a leaner, stronger body.
[1] References:
- Schoenfeld BJ et al., Effects of Resistance Training Frequency on Measures of Muscle Hypertrophy, Sports Medicine, 2016.
- Longland TM et al., Higher compared with lower dietary protein during an energy deficit combined with intense exercise promotes greater lean mass gain and fat mass loss, Am J Clin Nutr, 2016.
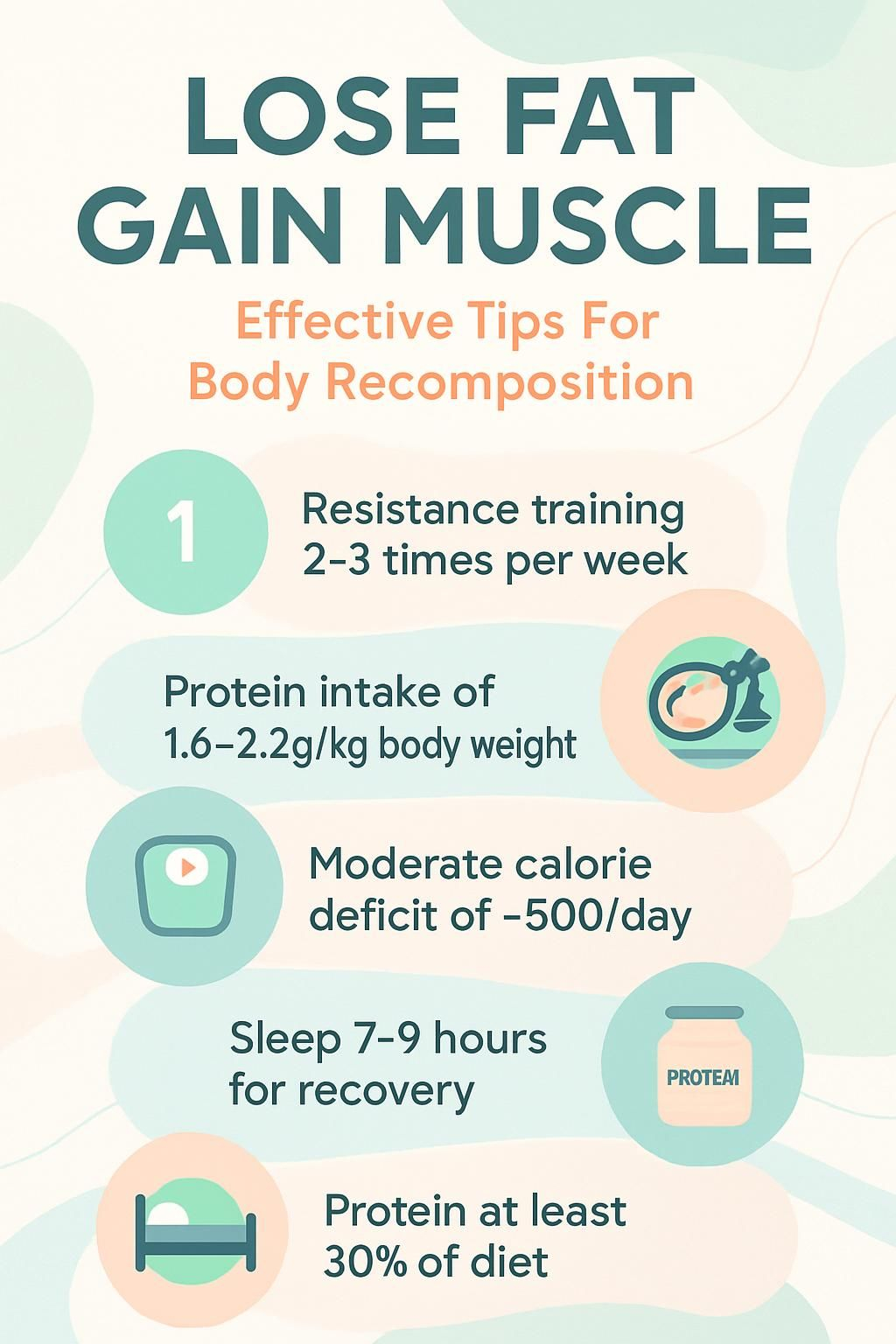
Key Takeaways
- Lift weights 2 to 3 days per week and eat 1.6 to 2.2 g protein per kilogram body weight. Studies show this combo helps you lose fat and build muscle.
- Use a moderate calorie deficit, about 500 calories per day. Pair it with progressive overload to lose around one pound per week while keeping lean mass.
- Track changes with DEXA scans, skinfold calipers, and progress photos. These tools reveal body composition shifts better than a scale alone.
- Protect recovery. Aim for 7 to 9 hours of sleep and manage stress to support hormones, repair muscles, and avoid overtraining.
- A common macro setup is at least 30% protein, around 40% carbs on training days, and healthy fats from fish, nuts, and olive oil.
Understanding Body Recomposition

Body recomposition means you reduce body fat while increasing lean muscle mass. You shift your ratio of fat to muscle, which improves health and performance even if your scale weight barely changes.
What does body recomposition mean?
You focus on changing what your body is made of, not just total weight. As fat drops and muscle grows, your shape, strength, and fitness improve.
Clothes may fit better and muscles look more defined, even with small weight changes. Research links higher protein intake and progressive overload, which means gradually harder training, with better muscle growth during fat loss.
Many lifters notice the biggest wins by combining steady lifting with daily protein targets. This plan keeps strength up while body fat slowly falls.
“Smart training with enough protein can add muscle while trimming fat at the same time.”
How can you lose fat and build muscle at the same time?
Use a slight calorie deficit so your body taps stored fat for energy. Support muscle growth with a high-protein diet. Protein synthesis, your body’s repair and build process, needs steady amino acids.
Eat 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. Choose whole foods such as eggs, yogurt, lean meats, beans, and whole grains to cover vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
Lift 3 days per week with compound moves, like squats, deadlifts, presses, rows, pull ups, and push ups. Add weight, reps, or sets over time to drive muscle hypertrophy, which is muscle growth.
Include cardio for heart health and extra calorie burn. Mix steady cycling, brisk walking, or intervals as needed. Measure progress with DEXA scans when possible, or use calipers and photos for consistency.
Steady routines over months work best. Many people report clear increases in lean mass on DEXA while body fat inches down.
Key Principles of Body Recomposition
Clear goals and simple habits guide your day to day plan. Training, nutrition, and recovery must support each other.
How does a calorie deficit help with fat loss?
A calorie deficit makes your body use stored fat for energy. If you eat fewer calories than you burn, fat loss follows over time.
A daily deficit near 500 calories often equals about one pound of fat loss per week. Your basal metabolic rate is what you burn at rest. Stay under your total maintenance calories to lose fat while you protect muscle with lifting and protein.
Tracking intake helps you stay consistent. Many people find a food scale and a simple log are enough to keep targets on track.
What is progressive overload and how does it build muscle?
Progressive overload means you increase training stress little by little. Add weight, do extra reps, or shorten rest. These changes force muscles to adapt, then grow stronger.
If you never raise the challenge, gains stall. Moving from 10 pound dumbbells to 12 pounds is a small step that restarts progress. Over weeks, these steps add up to bigger lifts and more muscle.
Write down your workouts. Seeing the trend helps you plan the next small jump and prevents plateaus.
Why is consistency important for body recomposition?
Results come from steady habits. Hit your protein target daily. Train on a set schedule, usually 3 days per week for strength, plus cardio as needed.
Small improvements stack up when you do not skip sessions. Track body weight weekly and compare with photos and strength logs. Drink enough water so workouts stay strong. Dehydration can reduce endurance and focus.
… References:
- Schoenfeld BJ et al., Effects of Resistance Training Frequency on Measures of Muscle Hypertrophy, Sports Medicine, 2016.
- Sawka MN et al., Exercise and fluid replacement, ACSM Position Stand, 2007.
Nutrition for Body Recomposition
Food drives both fat loss and muscle repair. Hit protein needs, fuel training with carbs, and include healthy fats for hormones and energy.
How does a high-protein diet support body recomposition?
Protein gives your muscles the building blocks they need to repair after training. It also helps you keep lean mass in a calorie deficit.
Aim for at least 1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight each day. Protein has a higher thermic effect than carbs or fats, so your body burns more energy digesting it. You stay fuller, which makes a deficit easier.
Whole foods should come first. Whey or plant protein powders can fill gaps when needed. This mix supports steady progress through your recomposition phase.
What is the best macronutrient balance for fat loss and muscle gain?
Pick calories to lose about 0.5 to 1 pound per week. This pace preserves strength and allows muscle growth if training is on point.
Many lifters do well with about 30% of calories from protein. Carbs often sit near 40% on training days to fuel hard sets and recovery. Healthy fats usually make up the rest, about 30%, which supports hormones and satiety.
This balance is a starting point. Adjust based on energy, hunger, and performance in the gym.
Which healthy fats provide energy during recomposition?
Choose fats that support heart and joint health. Good options include olive oil, avocados, almonds, walnuts, and fatty fish like salmon. These foods provide unsaturated fats that support recovery and steady energy.
Try to include omega 3 rich foods a few times each week. They may reduce soreness and help you bounce back for your next workout.
Why are carbohydrates important for workouts?
Carbs fuel training. They restore muscle glycogen, which is your stored workout energy. Low carbs can make heavy sets feel harder than they should.
Have a carb rich snack before lifting if sessions feel flat. Oats, rice, fruit, or yogurt work well and digest easily. Keep carbs higher on training days when you push bigger weights.
Effective Exercises for Body Recomposition
Exercises that train many muscles at once give you the most return for time and effort. Combine big lifts with focused accessories.
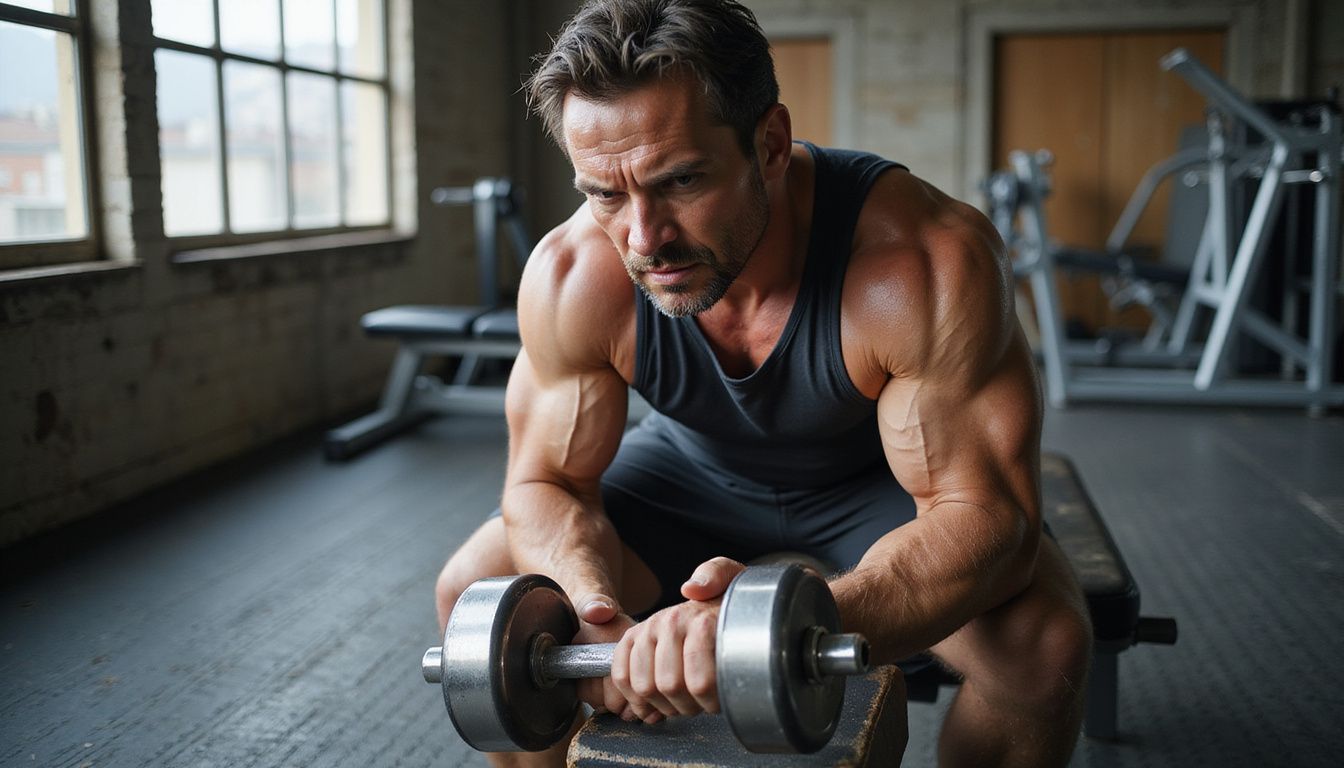
What are the essentials of resistance training?
Base your plan on compound movements. Squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and rows train multiple muscle groups together. Hit each major muscle group 2 to 3 times per week.
Use progressive overload to keep moving forward. Add isolation work, like curls and triceps extensions, to strengthen weak links. Good form lowers injury risk and keeps progress steady.
Track workouts and your body composition so you can adjust volume and intensity at the right time.
Which compound movements build muscle most effectively?
Squats, deadlifts, bench presses, overhead presses, and pull ups stand out. These lifts let you move more total weight than single joint moves, which drives muscle growth.
One squat session challenges your glutes, quads, hamstrings, and core. It also taxes your upper body for stability. That makes each rep efficient for fat loss and strength.
Focusing on these lifts helps you stay lean while still getting stronger, even in a calorie deficit.
How should you include isolation exercises in your routine?
Use isolation exercises after your main lifts. This timing saves energy for the heavy work and still targets lagging muscles.
Start with two or three sets per muscle group each week. Use slow, controlled reps so the target muscle does the work. Calf raises, lateral raises, and leg curls are useful examples.
What role does cardio play in losing fat?
Cardio increases calorie burn, which supports a calorie deficit. It also improves heart health and recovery between sets.
Choose options you enjoy, like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Aim for at least three sessions per week, adjusting duration to fit your goals and schedule.
Advanced Training Techniques
When progress slows, smart intensity methods can restart gains. Use them sparingly so recovery stays strong.
How does High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) aid recomposition?
HIIT uses short bursts of hard effort followed by brief rest. This raises your heart rate fast and keeps calorie burn high even after you finish.
Movements like sprints, kettlebell swings, or burpees stress muscles and build conditioning. Most HIIT sessions last 20 to 30 minutes, which fits busy days and supports fat loss.
What are effective progressive overload strategies?
- Add small weight increases, like 2.5 to 5 pounds on a barbell, every week or two.
- Grow total reps across sets, for example add one rep per set until you hit the top of your target range.
- Control tempo to raise time under tension, try three seconds down and three seconds up.
- Shorten rest on select moves, for example drop from 90 seconds to 60 seconds to increase effort.
- Train a muscle group twice per week instead of once to increase quality volume.
- Rotate similar movements, such as lunges for squats, to spur new adaptation.
- Log each session in an app or notebook to guide the next small jump.
- Use supersets or drop sets on occasion after your main work to challenge stubborn areas.
- Set one monthly personal best, even if it is a single extra rep or a small weight bump.
Writing down weights and reps shows where you are improving and where you are stuck. That clarity makes changes simple and targeted.
How can supersets and drop sets enhance training?
- Supersets pair two exercises with little rest, which saves time and raises intensity.
- Drop sets reduce weight after reaching fatigue so you can keep going and recruit more muscle fibers.
- Both methods increase total work in a short window, which supports strength and muscle growth.
- They also keep heart rate higher, adding a small boost to calorie burn.
- Use them once or twice per week so recovery does not suffer.
- Master technique first. Advanced methods work best on a base of solid form.
These tools are helpful finishers. Keep your main lifts steady, then add intensity where it fits your plan.
Tracking Progress in Body Recomposition
Measuring the right things keeps you motivated. It also helps you adjust quickly when progress slows.
How can you monitor your body fat percentage accurately?
Home body fat scales offer estimates that can vary. For precise data, use DEXA scans or hydrostatic weighing when you can.
Skinfold calipers can work well if you measure the same sites each time. Take readings every four weeks and add front, side, and back photos under the same light.
These methods show change even when scale weight stalls. Seeing proof keeps you consistent.
Why should you use progress photos during recomposition?
Photos capture changes that numbers miss. Muscle can grow while fat drops, so weight may hold steady.
Take monthly shots from the same angles in similar lighting. Comparing images side by side reveals slow but steady body changes.
How do you track strength improvements effectively?
Use a training log to track sets, reps, and weights. Then aim to beat one number each week, like one more rep or a small weight increase.
Test key lifts monthly, such as squats or deadlifts. A 2.5 to 5 percent jump in load or reps signals true muscle gain and better neuromuscular efficiency.
^1 American College of Sports Medicine, Progression Models in Resistance Training for Healthy Adults, 2020.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Small errors can stall progress for weeks. Avoid these common traps so your effort pays off.
What are the risks of overtraining?
Too much training with too little rest raises injury and illness risk. You may feel sore all the time, sleep poorly, or see performance drop.
High cortisol, a stress hormone, can rise during overtraining. That shift may slow fat loss and reduce muscle growth even with hard work.
Plan rest days and lighter weeks to recover. If motivation crashes and lifts slip, pull back and sleep more.
… 1: Meeusen R et al., Prevention, diagnosis and treatment of the Overtraining Syndrome, European Journal of Sport Science, 2013.
How can undereating cause muscle loss?
Eating far below your needs can lead to muscle breakdown. In long deficits with low protein, a chunk of weight loss can come from lean tissue.
Warning signs include dropping strength, slower recovery, and constant hunger. Keep protein high, spread meals through the day, and keep training heavy to defend muscle.
Why is recovery and sleep often neglected?
Busy schedules and pressure for quick results push people to train more and rest less. That approach backfires.
Muscles grow during sleep and rest periods, not during the lift itself. Adults need 7 to 9 hours of quality sleep to support hormones, fat loss, and repair.
Summary: Recovery habits are simple but easy to skip. Prioritize them if you want steady change.
Importance of Recovery
Think of recovery as the bridge between workouts and results. It turns hard effort into strength and muscle.
How does sleep influence muscle growth?
Deep sleep boosts growth hormone, which supports muscle repair. Short sleep raises cortisol and can slow recovery.
Aim for a consistent bedtime and a cool, dark room. Many lifters notice less soreness and better performance after a week of solid sleep.
Summary: Sleep helps you rebuild and perform. Treat it like a key part of training, not a bonus.
Why is stress management crucial for results?
Chronic stress keeps cortisol high, which can increase fat storage and reduce protein synthesis. That makes recomposition harder.
Use simple tools like breathing drills, walks, or short breaks from screens. Track your mood to spot patterns that hurt training or diet.
Summary: Lower stress, recover faster, and lift better. Small daily habits add up.
What are the benefits of active recovery days?
Active recovery uses light movement to boost blood flow without adding strain. Walks, easy cycling, or yoga reduce soreness and support mobility.
Many people return to heavy lifts feeling fresher after an active rest day. Keep it easy, about 20 to 40 minutes, and finish feeling better than when you started.
Supplements to Support Body Recomposition
Supplements can fill gaps. They do not replace whole foods, training quality, or sleep.
How do protein powders help with muscle gain?
Protein powders offer a fast way to hit your daily protein target. A typical serving provides 20 to 30 grams, which supports muscle protein synthesis after lifting.
Both whey and quality plant options work well. Many people find a shake after training helps them reach 1.4 to 2.0 grams per kilogram of body weight per day.
[1] Pasiakos SM et al., J Am Coll Nutr, 2015. International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand, Protein and Exercise, 2017.
What benefits does creatine provide for recomposition?
Creatine increases strength and training volume. That extra work builds more lean mass over time.
It also helps you recover between hard sets by restoring quick energy in muscle cells. Many lifters add 3 to 5 grams per day and see clear strength gains within weeks.
Should you use Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs)?
BCAAs may reduce soreness for some people. If your protein intake is already high, extra BCAAs rarely add much.
They can help if your daily protein is low or you have long gaps between meals. Most find whole foods or whey more cost effective.
When to Seek Expert Guidance
Professional support can speed up results and prevent trial and error. It also helps if you have health conditions.
When should you consult a nutritionist or dietitian?
If fat loss stalls, energy crashes, or you have medical needs, talk with a registered dietitian. They can assess your intake, lab values, and body composition, then adjust your plan.
Signs like constant fatigue, digestive problems, or hair changes can point to nutrient gaps. A tailored plan can restore energy and lift performance.
How can a personal trainer assist your goals?
A trainer builds a plan that fits your schedule, equipment, and goals. You get coaching on form to stay safe and drive progress.
They also track your strength and body composition, then make timely changes. Many people see faster results with expert feedback.
[^1]: Schoenfeld BJ et al., Effects of Resistance Training Frequency on Measures of Muscle Hypertrophy, Sports Medicine 46, 2016.
What are professional assessments like DEXA scans used for?
DEXA scans measure body fat, lean mass, and bone with high accuracy. They show if weight changes come from fat or muscle.
Coaches use these results to tweak calories, macros, and training. If precision matters to you, DEXA offers clear data to guide next steps.
Conclusion
Body recomposition takes patience and a plan. Lift with progressive overload, eat enough protein, and maintain a small calorie deficit. Track progress with photos, strength logs, and, when possible, DEXA.
Prioritize sleep and stress control so your training pays off. Stay consistent and adjust slowly. This article is for education, not medical advice, so check with a healthcare professional if you have health concerns. With steady work, you can build muscle, lose fat, and feel stronger week by week.
FAQs
1. What is body recomposition and how does it help with losing fat and gaining muscle?
Body recomposition refers to the process of reducing stored energy while increasing lean tissue at the same time. Studies show that combining resistance training with a protein-rich eating plan supports this goal by promoting muscle growth as you lose excess weight.
2. How much protein should I eat for effective body recomposition?
Research suggests consuming 0.7 to 1 gram of protein per pound of body mass each day helps maintain and build lean tissue during fat loss efforts. For example, a person weighing 150 pounds would aim for about 105 to 150 grams daily.
3. Can cardio exercise support my goal to lose fat and gain muscle?
Cardio activities like brisk walking or cycling can increase total calories burned, which aids in reducing stored energy reserves. However, strength training remains essential because it signals your system to keep building new fibers even as you shed unwanted weight.
4. Is it possible for beginners to see faster results in body recomposition compared to experienced athletes?
Beginners often experience quicker changes due to their bodies’ initial response when starting structured workouts paired with improved nutrition habits; studies confirm these early gains tend to slow over time as adaptation occurs.
Summary: Body recomposition involves lowering stored energy while adding lean tissue through targeted movement routines and proper nutrient intake, especially adequate protein amounts alongside regular resistance work; beginners may notice progress more quickly than those who have trained longer according to current research findings.







