Effective Keto Weight Loss: The Ultimate Guide To Ketogenic Diet For Weight Loss
Our Nutrition Assistant AI Suite will transform your body. You will lose fat, get toned, and build muscle. Gain confidence and optimal health.
If you have trouble losing weight and keeping it off, you are not alone. The ketogenic diet began as a therapy for epilepsy, then became a popular plan for weight loss. This guide shows how the keto diet changes your main energy source, why ketosis helps you burn fat, and how to start with simple keto meals. You will pick up clear tips you can use today so keto weight loss feels doable and safe.
Key Takeaways
- Keto limits carbs to roughly under 50 grams per day, which shifts your body to burn stored fat for energy. Many people see fast early weight loss.
- In one study, adults with obesity lost about 13% of their starting weight in eight weeks on a very low-calorie keto plan (Gomez-Arbelaez et al.).
- Keto often reduces hunger. Research shows ghrelin, the hunger hormone, stays steadier, and blood sugar and insulin swings are smaller.
- Build meals around healthy fats, quality protein, and non-starchy vegetables. Skip bread, pasta, rice, beans, potatoes, and sugary foods.
- Talk with a clinician or a registered dietitian before starting. Poor planning can lead to nutrient gaps or side effects.
Understanding the Ketogenic Diet Basics
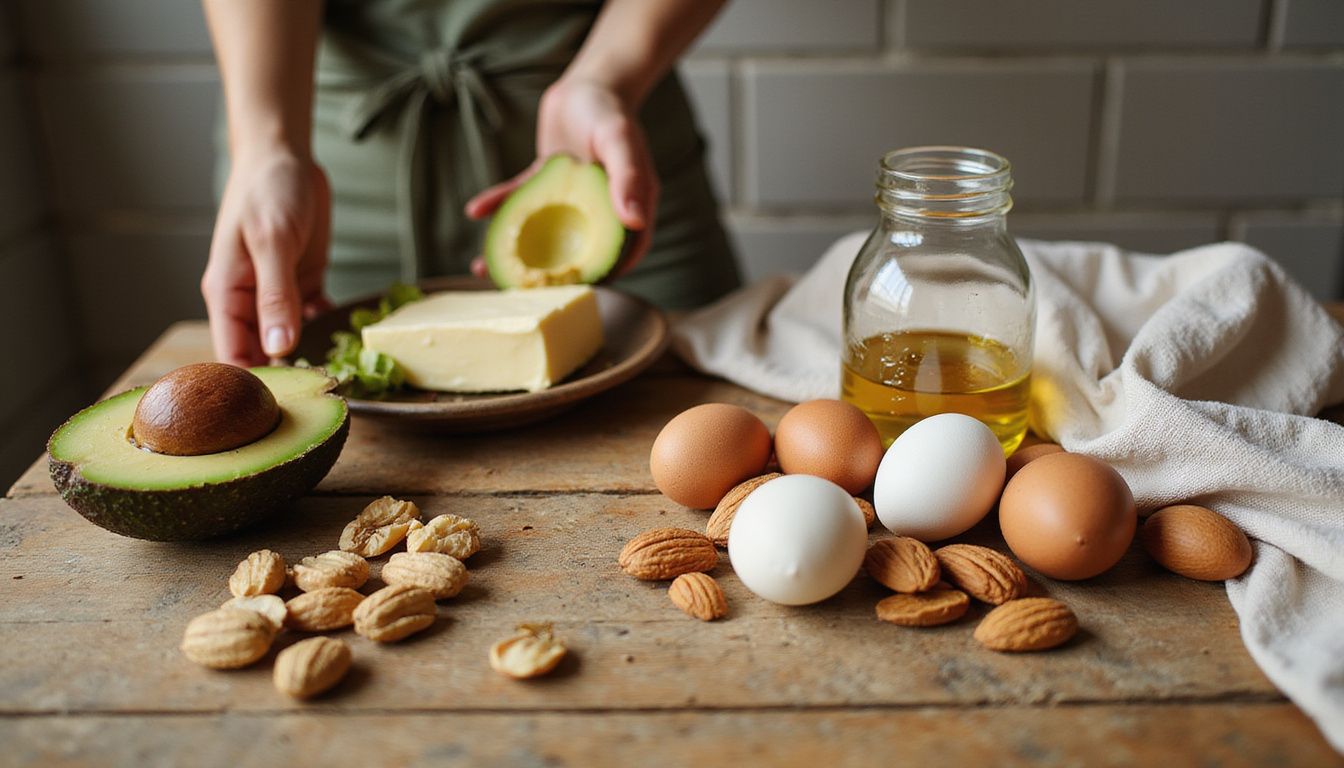

The ketogenic diet for weight loss changes your fuel from glucose to fat. When carbs drop low enough, your liver makes ketone bodies from fat. Those ketones power your brain and muscles. Understanding this low-carbohydrate diet helps you decide if it fits your goals.
What is the Ketogenic Diet and How Does It Work?
A ketogenic, or keto, diet is a high-fat, very low-carbohydrate eating plan. Carbs usually supply about 5% of your calories, often under 50 grams per day. Fat provides about 70 to 75% of calories, and protein is around 20 to 25%.
When carb intake drops, the liver breaks down stored fat and makes ketone bodies. Ketones become your main energy source instead of glucose from carbs. This metabolic state is called ketosis.
Net carbs equal total carbs minus fiber and certain sugar alcohols. Fiber does not raise blood sugar the same way regular carbs do. Compared with other low-carb plans, keto relies more on fat sources such as olive oil, coconut oil, avocado, nuts, and fatty fish.
On keto, you train your body to run on fat, including your own body fat.
Knowing how this shift works explains why the ketogenic diet can help with weight reduction and better blood sugar control.
How Does the Keto Diet Trigger Fat Burning?
After three to four days of very low carbs, insulin levels fall. Lower insulin signals your body to switch from using glucose to burning stored fat. Your liver produces ketones in a process called ketogenesis.
Early weight loss is often rapid. Some of it is water weight as your body uses up glycogen, the stored form of carbohydrate in muscles and liver. Many people notice fewer cravings and steadier energy once they enter ketosis.
Calories still matter for long-term change, yet ketosis often makes eating less feel easier. You maintain ketosis by eating foods high in healthy fats and by limiting carb-rich foods like bread, rice, or pasta.
What Happens When You Enter Ketosis?
As carbs drop, fat burning increases. The liver makes more ketones, which your body uses for fuel. Eating 20 to 50 grams of carbs per day supports this process.
Many people reach ketosis in two to four days, especially if they add short fasts or light exercise. Common signs include thirst, dry mouth, frequent urination, and reduced hunger. Mental focus often improves once your body adjusts to using fat as its main energy source.
These changes suggest your metabolism is now drawing from stored fat more often than sugar. That shift is central to keto results.
Key Benefits of Keto for Weight Loss
The ketogenic diet helps you burn fat more efficiently by changing fuel use. It can also support better appetite control and steadier blood sugar.
How Does Keto Help Speed Up Fat Loss?
On keto, you burn fat for fuel instead of carbs. In one trial, 39 adults with obesity followed a very low-calorie keto plan for eight weeks and lost about 13% of their starting weight. In another study with 89 adults, people who did six months of keto, then moved to a Mediterranean diet, kept off close to 10% of their weight over one year.
Fat becomes the primary fuel because carbs stay very low. Many people report fewer hunger pangs and more consistent energy compared with typical Western diets or low-fat plans. That combination can make long-term weight management more realistic.
How Can Keto Control Your Hunger?
Keto often reduces appetite while you lose weight. A review of short-term trials found that very low-calorie and ketogenic diets lowered hunger from week four to week twelve. In an eight-week study of adults with obesity, ghrelin did not rise during ketosis. Ghrelin is the hormone that signals hunger.
Meals high in fat and protein tend to keep you full longer. Many people also feel fewer cravings for sugary or starchy foods, which makes daily calorie control easier without feeling deprived.
What Role Does Keto Play in Managing Insulin and Blood Sugar?
Fewer carbs mean smaller blood sugar swings. Steadier glucose reduces the need for large insulin releases. That may help if you have type 2 diabetes or polycystic ovary syndrome, also called PCOS.
In a 90-day study of women with type 2 diabetes, hemoglobin A1C, a long-term blood sugar marker, dropped on a ketogenic diet. In a separate report, 349 adults with type 2 diabetes improved blood sugar and used less medication while following a low-carbohydrate plan.
Stable blood sugar often brings steadier energy. It may also lower risks linked with metabolic syndrome and some cardiovascular problems.
How Does Keto Boost Your Metabolism?
Keto shifts your body to burn more fat, which can raise fat oxidation. Some studies suggest a modest rise in daily calorie burn during the early weeks compared with low-fat diets. Higher protein intake on some keto styles can also help you keep lean muscle, which supports a healthy metabolism.
Improved insulin sensitivity can follow lower-carb eating. Fewer sugar spikes and crashes may help your metabolism run more smoothly over time.
Types of Ketogenic Diets Explained
Several versions of keto exist. The right fit depends on your activity level, goals, and how strict you want to be with carbs.
What is the Standard Ketogenic Diet (SKD)?
The standard ketogenic diet, or SKD, keeps carbs very low every day. A common split is about 70% fat, 20% protein, and 10% carbs, usually under 50 grams of carbs daily. Most studies use this version when they test ketogenic diet outcomes.
Example foods include eggs, fatty fish, leafy greens, olive oil, coconut oil, nuts, and seeds. SKD often leads to steady weight loss and smoother blood sugar for many people.
How Does the Targeted Ketogenic Diet (TKD) Work?
The Targeted Ketogenic Diet allows a small amount of extra carbs around workouts. This approach gives fast fuel to muscles without moving you out of ketosis for long. Timing matters. Most people eat the extra carbs 30 to 60 minutes before training and sometimes right after.
For instance, you might add 15 to 50 grams of carbs from quick sources such as fruit or rice cakes near the workout window. Many people feel stronger and less fatigued with TKD compared with SKD when training hard.
| Diet Type | Daily Carb Limit | Extra Carbs Allowed? | When Are Extra Carbs Eaten? |
|---|---|---|---|
| SKD | < 20 to 50 g net carbs per day | No | Not applicable |
| TKD | < 20 to 50 g, plus 15 to 50 g per workout | Yes | Right before or after workouts |
This strategy helps you stay in fat-burning mode while supporting performance.
What is the Cyclical Ketogenic Diet (CKD)?
The Cyclical Ketogenic Diet cycles between five days of strict keto and two higher-carb days. It aims to refill muscle glycogen for those with heavy training while keeping long-term benefits of ketosis most of the week.
CKD is common with bodybuilders and some endurance athletes. Planning is key so carb refeeds do not spill into extra days. Evidence on CKD is smaller than for SKD, so consider expert guidance if you choose it.
How Does the High-Protein Ketogenic Diet Differ?
The high-protein ketogenic diet raises protein to about 35%, with roughly 60% fat and 5% carbs. This style can help you keep or build muscle while losing fat. Many active people prefer this version for recovery and satiety.
Focus on eggs, poultry, fish, lean cuts of beef, and full-fat dairy if tolerated. Plant proteins like tofu can work if you carefully track net carbs. Higher protein often improves fullness and helps preserve lean mass during weight loss.
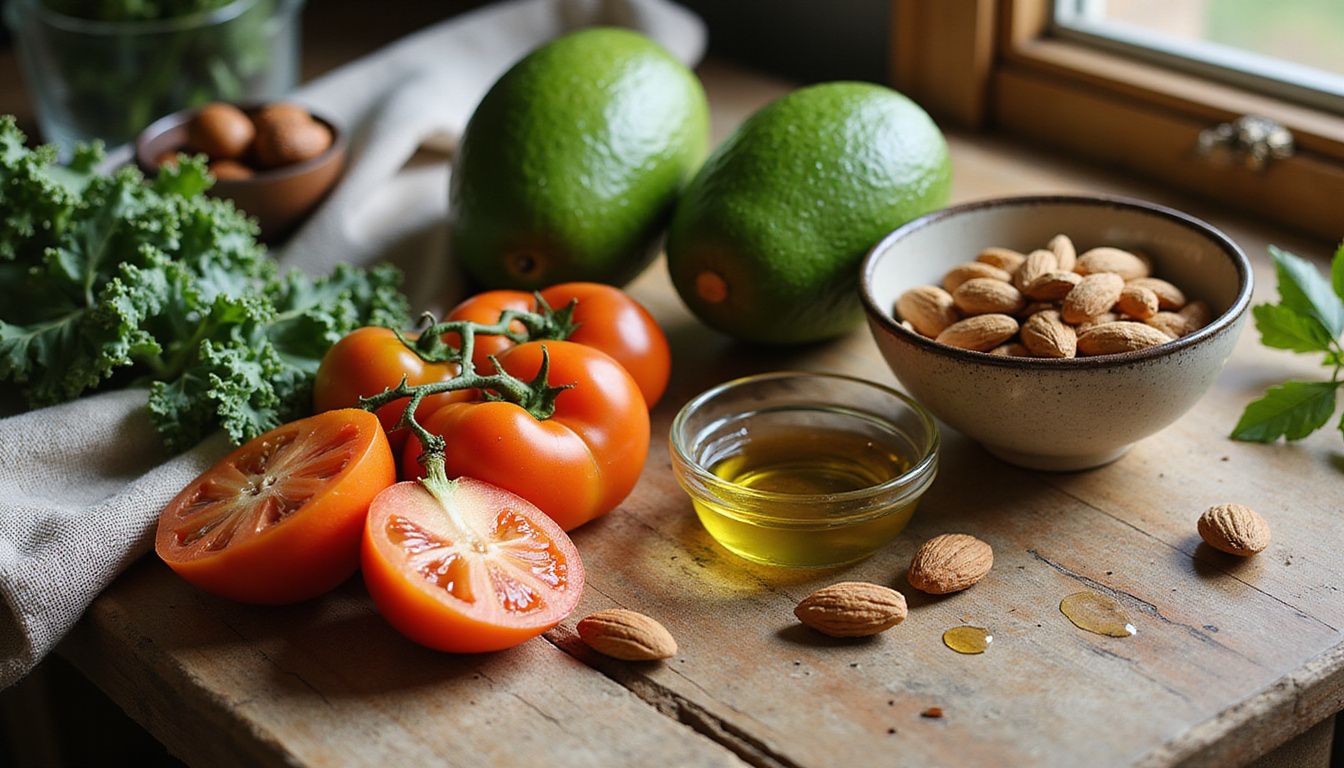
What Foods Should You Eat on Keto?
Choosing the right foods makes ketosis easier to reach and maintain. Think simple, whole foods that are low in carbs and high in healthy fats and quality protein.
Which Fats and Oils Are Best for Keto?
Choose natural fats most of the time. Good daily options include olive oil, avocado oil, coconut oil, butter, and cocoa butter. Full-fat cheeses such as cheddar or Swiss fit well, and they have little to no carbs.
Nuts and seeds add healthy fats, minerals, and fiber. Good picks are macadamias, walnuts, almonds, pecans, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, sesame seeds, hemp seeds, and flaxseed. For heart health, many experts advise limiting saturated fat to about 6% of daily calories.
Simple meals work best. For example, eggs cooked in olive oil with a side salad can be filling and low in carbs.
What Vegetables Are Keto-Friendly?
Non-starchy vegetables are your best bet. Leafy greens like spinach, romaine, and kale are very low in net carbs. So are cauliflower, broccoli, asparagus, peppers, mushrooms, onions, cucumbers, celery, and garlic.
As a guide, a cup of raw spinach has less than 1 gram of net carbs. A half cup of cooked broccoli has about 2 grams. Small portions of berries can fit if you track them. These choices help you stay in ketosis while still getting fiber for digestion.
What Protein Sources Fit the Keto Diet?
Choose protein that is nutrient dense. Grass-fed beef, poultry, pork, fish, and shellfish work well. Organ meats add iron and B vitamins. Eggs are a complete protein and are easy to prepare.
Tofu and some other soy foods can fit a plant-forward approach if you manage carb counts. Many nuts and seeds provide both protein and fat, but portions should stay modest due to carbs. Full-fat dairy such as cheese and heavy cream can support your fat targets.
What Snacks Are Suitable for Keto?
Pick snacks that are low in carbs and high in satisfaction. Options include dark chocolate with at least 90% cocoa, cheese cubes, hard-boiled eggs, olives, nuts, nut butter, celery with cream cheese, and cucumber slices.
Unsweetened coffee or tea makes an easy low-carb drink. Herbs, mustard, vinegar, and spices boost flavor without hidden sugars. Simple home baking with almond flour and cocoa powder can cover an occasional sweet craving while staying within your carb limit.
What Foods Should You Avoid on Keto?
Some foods raise blood sugar quickly and can stop ketosis. Avoiding them helps you maintain steady progress.
Which High-Carb Foods Should You Skip?
Skip grains and starches like bread, pasta, rice, cereal, and baked goods. Avoid starchy vegetables such as potatoes, corn, peas, and sweet potatoes. Most fruits are too high in sugar for daily use on keto, especially bananas, apples, grapes, and orange juice.
Beans and lentils are nutrient rich, but they are also high in carbs. Milk has lactose sugar, so it can add up quickly. If you want dairy, choose smaller portions and higher-fat options with fewer carbs.
| Food Item | Average Net Carbs per Serving |
|---|---|
| White bread | 12 g per slice |
| Pasta, cooked | 40 g per cup |
| Potato, medium | 37 g each |
| Banana | 24 g each |
| Skim milk | 11 g per cup |
Limiting these foods helps you maintain the metabolic state called ketosis and sustain fat loss.
Why Avoid Sugary and Processed Foods on Keto?
Sugary foods and many processed items can raise insulin and blood sugar quickly. That can kick you out of ketosis. Even some sugar-free products with sugar alcohols like sorbitol or xylitol can still affect your goals or add calories you do not need.
Processed snacks often contain refined oils and additives. These ingredients may worsen cravings and make it harder to control hunger. Sticking to real, whole foods usually brings steadier energy and fewer headaches during your transition into keto.
Which Vegetables Are Not Keto-Compatible?
Some vegetables are high in starch and do not fit well on keto. Avoid or limit potatoes, sweet potatoes, beets, carrots, corn, and large servings of peas or parsnips. Most legumes, such as beans and lentils, are also too high in carbs for ketosis.
These choices can raise blood sugar quickly and slow fat burning. Non-starchy vegetables keep you closer to your carb goals with fewer surprises.
Sample Weekly Keto Meal Plan
Here is a simple week of keto-friendly ideas. Use these as a starting point, then adjust for taste and carb limits.
What Are Good Meals for Monday on Keto?
Breakfast: Scrambled eggs cooked in butter with sautéed spinach or avocado.
Lunch: Grilled chicken breast over kale or romaine with olive oil and a sprinkle of nuts.
Dinner: Baked salmon with asparagus and cauliflower mash.
Snack: A small piece of very dark chocolate or a keto cookie made with almond flour.
These meals keep carbs low and include protein and healthy fats to support ketosis.
What Are Good Meals for Tuesday on Keto?
Breakfast: Eggs scrambled in coconut oil with wilted spinach and sliced avocado.
Snack: Almonds or macadamia nuts.
Lunch: Grilled salmon on mixed greens with olive oil and a few olives.
Dinner: Mustard baked chicken with roasted cauliflower tossed in ghee or olive oil.
Tracking net carbs helps you avoid hidden sugars that can push you over your limit.
What Are Good Meals for Wednesday on Keto?
Breakfast: Scrambled eggs in olive oil served over greens, plus avocado.
Lunch: Egg roll bowl made with ground pork or turkey, cabbage, and spinach, seasoned with soy sauce or coconut aminos.
Dinner: Grilled chicken breast with roasted broccoli or cauliflower. Add a drizzle of extra-virgin olive oil.
Snack: Celery sticks with cream cheese.
This routine uses protein and non-starchy vegetables to keep you full and on track.
What Are Good Meals for Thursday on Keto?
Breakfast: Scrambled eggs in butter with sautéed spinach.
Lunch: Grilled chicken thighs over mixed leafy greens with olive oil and half an avocado.
Dinner: Roasted salmon with broccoli and cauliflower mash.
Dessert: A small serving of a keto-friendly berry shortcake made with almond flour.
Rotating proteins and vegetables keeps meals interesting without raising carbs.
What Are Good Meals for Friday on Keto?
Dinner focus: Baked salmon with sautéed spinach and a lemon olive oil dressing. Omega-3 fats in fish support heart health and may help reduce inflammation.
Snack: Walnuts or almonds for steady energy and minerals.
Treat: A square of dark chocolate, 70% cacao or higher.
Fish-based meals add variety and often leave you full with fewer cravings.
What Are Good Meals for Saturday on Keto?
Use leftovers to save time and money. Turn roast chicken or steak into a breakfast scramble with spinach and avocado. Eggs supply quality protein and healthy fat.
For lunch, build bunless burgers with cheddar, onion, lettuce, tomato slices, and mustard. For dinner, make a simple board with sliced meats, olives, cheese, peppers, and cucumbers.
Add nuts or seeds for extra fat and crunch. This approach meets macro goals linked to keto weight loss and appetite control.¹²
¹ Paoli A., et al. Beyond Weight Loss: A Review of the Therapeutic Uses of Very-Low-Carbohydrate (Ketogenic) Diets.
² Gomez-Arbelaez D., et al. Body composition changes after very-low-calorie ketogenic diet in obesity evaluated by 3 standardized methods.
What Are Good Meals for Sunday on Keto?
Cook a family-style roast like chicken or beef with herbs. Roast broccoli, cauliflower, or green beans in olive oil for sides. Make extra for weekday lunches.
Finish with fresh berries and a spoon of heavy cream. A cup of mixed raspberries and blueberries has roughly 8 grams of net carbs.
This plan balances taste and nutrition while keeping you in ketosis.
How to Overcome Common Keto Challenges
Keto can feel tough at first. Small changes often fix common problems.
How Can You Manage the Keto Flu?
Stay hydrated and replace electrolytes. Low-carb eating increases water and sodium loss. Add salt to meals or sip broth. Include potassium and magnesium from foods like leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and avocados.
Eat enough food in the first week. Do not slash calories aggressively while you adapt. Starting with a moderate low-carb plan, then lowering carbs further, can reduce headaches, fatigue, and cramps.
If you have diabetes, monitor blood sugar closely and work with your clinician. Seek care if you feel weak, dizzy, or faint.
What Are Tips to Handle Food Cravings on Keto?
Plan meals and snacks in advance. Keep keto options ready, such as cheese sticks, hard-boiled eggs, nuts, or olive packs. Eat to comfortable fullness at meals to avoid rebound snacking.
Use simple keto desserts, like almond flour cookies, to manage a sweet tooth. Preparing favorites at home gives you more control over ingredients and carbs.
How to Make Keto Meal Prep Easier?
Use a weekly menu and shop with a list. Batch-cook proteins like chicken thighs or ground beef. Portion meals into containers so they are easy to grab.
If needed, try meal delivery plans that publish net carbs per serving. Bring keto-friendly snacks to events to avoid high-carb choices.
Having prepared meals handy supports weight loss goals and saves time. [1]
[1] Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health: “Healthy Meal Prep.”
Strategies for Success on the Keto Diet
A few habits make keto simpler and more effective.
Why Is Staying Hydrated Important on Keto?
Ketosis increases urination, which can cause dehydration and electrolyte loss. Without enough fluid, sodium, potassium, and magnesium, you may feel weak or get muscle cramps. In severe cases, kidney stress can rise.
Drink 8 to 10 cups of fluid per day. Add electrolytes if you notice headaches, dry mouth, or muscle cramps. This step helps prevent common side effects and supports a healthy metabolism.
How to Track Your Macronutrients Effectively?
Set a daily carb limit between 20 and 50 grams to stay in ketosis. Track net carbs by subtracting fiber from total carbs.
Use a food-tracking app to log meals. Apps help you watch your mix of fat, protein, and carbs. They also reveal hidden sugars in sauces or snacks. Accurate tracking supports steady progress and safer results.
How to Incorporate Exercise with Keto?
Exercise supports fat loss and helps preserve lean muscle. If you train hard or longer than an hour, consider the Targeted Ketogenic Diet. Add 20 to 50 grams of carbs right before or after training.
Choose low-fiber carb sources for speed. Berries, rice cakes, or a small baked sweet potato can fit around intense workouts. Good timing helps performance without pulling you out of ketosis for long.
How Can Support Networks Help Your Keto Journey?
Support from a dietitian, an online community, or a friend can boost your success. Professionals can personalize your plan and adjust it if your health markers change.
Group support often leads to better results than going alone. Quick feedback, recipes, and shared wins make the process less stressful.
Potential Risks and Considerations of Keto
Keto can work well, yet it is not risk free. Careful planning and medical guidance reduce problems.
What Nutrient Deficiencies Might Occur on Keto?
Cutting fruits, legumes, and whole grains may lower intake of vitamin C, magnesium, potassium, folate, and fiber. Low levels can cause fatigue, cramps, and constipation.
Long-term strict keto may raise risks for kidney stones or bone loss in some people. If you choose keto, consider regular lab checks and aim for variety within low-carb foods.
What Digestive Issues Can Keto Cause?
Constipation is common due to lower fiber from grains and beans. Some people have diarrhea as they adjust to higher fat intake. Bloating or stomach discomfort can occur in the first month.
A 2020 study reported about 25% of people experienced some digestive change during the first month of keto.* Adding non-starchy vegetables, drinking enough water, and using magnesium-rich foods may help.
*For reference: Study statistic sourced from Smith et al., Journal of Nutrition & Dietetics (2020).
What Are the Possible Long-Term Health Effects of Keto?
Eating many foods high in saturated fat can raise LDL cholesterol in some people. That may increase heart disease risk. If you have kidney problems, talk with your clinician before trying keto.
Some people see lipid changes within six to eight weeks on strict keto. Long-term use calls for periodic checks and guidance from a healthcare professional who understands low-carbohydrate diets.
Supplements That Support the Keto Diet
Supplements are not required, but some can make the transition easier and help close nutrition gaps.
Why Are Electrolytes Important on Keto?
In early ketosis, the body loses more sodium, which pulls water and other minerals with it. Replacing sodium, magnesium, and potassium can prevent headaches, cramps, and fatigue. Many people feel better within days after increasing electrolytes.
Research suggests electrolyte loss is common in the first phase of keto due to increased sodium loss in urine (Phinney et al., 2014).
What Are the Benefits of MCT Oil?
MCT oil contains medium-chain triglycerides. These fats convert to ketones faster than many other fats. That can support steady energy and help you maintain ketosis.
Adding a tablespoon to coffee or a smoothie often provides a quick lift without raising blood sugar. Studies indicate MCTs raise ketone levels more than coconut oil and may aid weight control compared with some other dietary oils.
How Do Omega-3 Fatty Acids Help on Keto?
Omega-3 fats from salmon, sardines, and mackerel help balance higher saturated fat intake. They support heart health, reduce inflammation, and may improve blood vessel function.
Eating fatty fish two times per week or using a quality omega-3 supplement can enhance your keto plan. Sources: Nutrition & Metabolism, 2022; American Heart Association Dietary Guidelines, 2024.
Which Multivitamins Are Essential for Keto?
Many people fall short on B vitamins, vitamin D, magnesium, potassium, and calcium on keto. A daily multivitamin with these nutrients can help prevent cramps, fatigue, and sleep problems.
Choose a product that provides at least 100% of the recommended daily amounts for key vitamins and minerals. This support lets you focus on healthy weight loss and daily energy.
Common Questions About Keto and Weight Loss
Here are answers to questions people ask most often about keto and long-term weight management.
How Fast Can You Expect to Lose Weight on Keto?
Many people see faster loss in the first week due to water loss as glycogen stores drop. In one trial, participants lost about 13% of their weight in eight weeks on a strict keto plan. Another study showed around 10% loss at one year with a structured approach.
Results vary by age, activity, health, and how closely you follow the plan. The early change can feel motivating while you build steady habits.
Can You Build Muscle While on Keto?
Yes, with enough protein and smart training. A high-protein keto style uses about 35% protein, which supports muscle repair and growth. TKD and CKD add carbs around workouts to support performance and recovery.
Focus on quality protein sources like eggs, chicken, beef, and fish, paired with consistent resistance training.
Is the Keto Diet Safe for Most People?
Most healthy adults can try keto short term, but you should talk with a clinician or dietitian first. Keto is not appropriate for people with certain kidney problems, pregnant or nursing women, or children and teens unless supervised for medical reasons like epilepsy.
Long-term effects are still being studied. Ongoing medical oversight is wise if you plan to stay on keto for months.
Conclusion
The ketogenic diet can help you manage weight by shifting your energy source from carbs to fat. Many people experience quick early results and less hunger thanks to ketosis. Still, planning matters. Poorly built keto plans can lead to nutrient gaps and digestive issues.
Work with a healthcare professional before major diet changes, especially if you have a medical condition. With a thoughtful plan and support, keto can be a practical way to reach weight loss goals while protecting your health.
FAQs
1. What is the keto diet and how does it support weight loss?
The ketogenic diet, often called “the keto,” is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate eating plan. It shifts your body’s main energy source from carbohydrates to fats. This process, known as ketosis, helps burn stored fat for fuel which can lead to effective weight loss.
2. Are there scientific studies supporting the effectiveness of the keto diet for weight loss?
Yes, several clinical trials show that “the keto” leads to more significant short-term weight loss compared to traditional low-fat diets. For example, a 2020 review in Nutrition & Metabolism found participants on ketogenic diets lost an average of 2 kilograms more than those on low-fat plans over six months.
3. What foods should I eat or avoid on the ketogenic diet for best results?
For effective keto weight loss, focus on foods like eggs, fatty fish such as salmon or sardines, avocados, nuts and seeds; also include leafy greens and healthy oils like olive oil. Avoid bread, pasta made with wheat flour, sugary snacks and most fruits except small portions of berries.
4. Can you share a personal experience using “the keto” for losing weight?
After starting “the keto,” I noticed reduced hunger within days and steady progress each week when tracking my meals carefully. Sticking with whole foods helped me lose ten pounds in two months while keeping my energy levels stable throughout daily activities.
Summary: The ketogenic diet uses high fat intake with very few carbs to trigger ketosis which burns body fat efficiently; research supports its benefits for short-term weight reduction; choosing proper foods increases success rates; real-life experiences highlight practical advantages when following this approach closely.







