Unlock Weight Loss Success With A High Protein Diet
Our Nutrition Assistant AI Suite will transform your body. You will lose fat, get toned, and build muscle. Gain confidence and optimal health.
If your current plan is stalling, you are not alone. A high-protein diet for weight loss can steady hunger, protect muscle, and make a calorie deficit easier to keep.
This guide explains the benefits, shows how much protein you need each day, and gives simple tips to choose protein foods that fit your life. If you want real progress, learn how to use protein intake to support steady weight loss.
Key Takeaways
- For weight loss, aim for 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight each day. This is higher than the RDA of 0.8 g/kg for adults (Mayo Clinic).
- Let protein provide 20% to 30% of daily calories during active weight loss. This range increases fullness and helps preserve muscle mass.
- Protein raises calorie burn through digestion, called the thermic effect. It can increase metabolism by 15% to 30%, while carbs raise it by about 5% to 10%.
- Choose lean meats, eggs, low fat dairy, legumes, and tofu. These protein sources deliver essential amino acids with less saturated fat, which helps manage cholesterol.
- If you have kidney or liver disease, talk with a healthcare provider first. High protein diets can add stress to these organs (Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, Mayo Clinic).
What Is a High-Protein Diet?
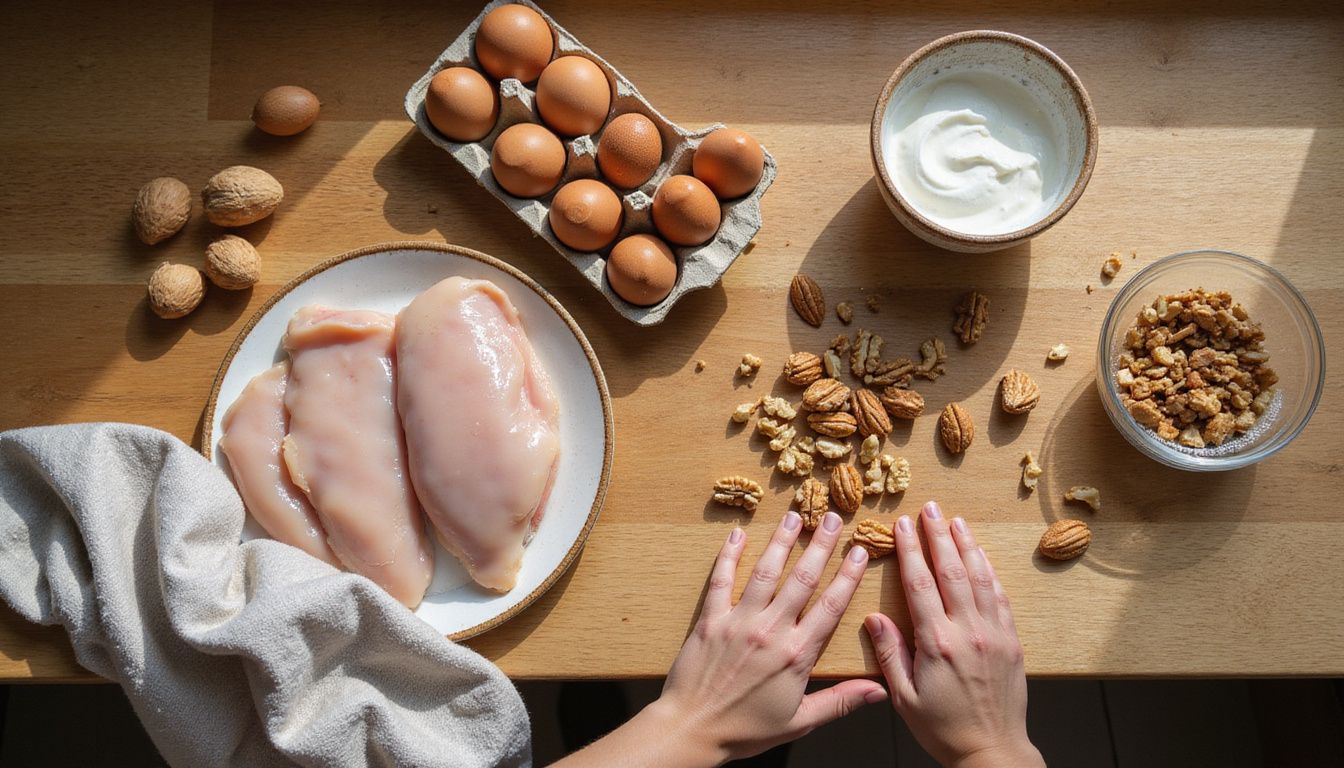

A high-protein diet shifts more of your daily calories to protein instead of relying mostly on carbohydrates or fats. Many diets for weight loss use this approach to curb appetite and maintain muscle.
What Does a High-Protein Diet Mean?
You eat more calories from protein than on a standard-protein diet. Many experts recommend 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight each day if your goal is fat loss or muscle maintenance.
For example, if you weigh 175 pounds, about 79 kilograms, a helpful range is roughly 127 to 174 grams of dietary protein per day. That is much higher than the RDA of 0.8 g/kg.
During weight loss, target 20% to 30% of total calories from protein. Both animal and plant protein can fit into a healthy high-protein diet plan.
To help you lose weight and prevent weight regain, increasing protein above the RDA can be beneficial.
How Is a High-Protein Diet Different from Other Diets?
High-protein diets raise your daily protein intake to about 20% to 30% of calories. You will eat more foods high in protein such as chicken, fish, eggs, beans, and Greek yogurt.
This approach often lowers carbohydrates compared with typical eating patterns that follow the Dietary Guidelines for Americans. In a standard balanced plan, carbs provide 45% to 65% of calories and fats about 25% to 35%. High-protein plans usually shift some calories away from carbs while keeping ample non-starchy vegetables and healthy fats.
Unlike carnivore diets, which are almost only animal foods with very few carbs, a high-protein diet includes plant proteins and lean meats along with whole grains and vegetables.
Some versions reduce grains or certain fruits, which can lower fiber and key nutrients if you do not plan well. Choosing nutrient-rich proteins over those high in saturated fat supports heart health and steady weight control.
How a High-Protein Diet Promotes Weight Loss
A high-protein diet for weight loss works through three main paths. It helps you feel full, it slightly boosts your calorie burn, and it protects the muscle that keeps your metabolism active.
How Does Protein Increase Satiety and Reduce Appetite?
Protein increases fullness by lowering hunger hormones and slowing digestion. It digests more slowly than carbs or fats, so you feel satisfied longer after meals.
Foods rich in protein, such as chicken, eggs, tofu, fish, dairy products, and beans, can reduce cravings and cut late-night snacking. Several reviews from the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics report that higher protein meals help people eat fewer calories across the day.
Divide your daily calories into four or five smaller meals with a good protein source each time. For example, a cup of Greek yogurt or cottage cheese in the afternoon can hold you to dinner better than chips.
How Does Protein Boost Metabolism?
Your body spends energy to digest food, called the thermic effect. Protein has the highest thermic effect, so it burns more calories during digestion than carbs or fat.
Research shows protein can raise metabolism by 15% to 30%, while carbs add about 5% to 10%. This extra burn helps you maintain a calorie deficit, which supports fat loss.
Protein also supports muscle growth and maintenance. Muscle tissue uses more energy at rest than fat tissue, so preserving it can help you maintain your target body weight.
Simple example: add chicken breast or Greek yogurt to lunch. Many people find they stay full longer and keep energy steadier through the afternoon.
How Does Protein Help Preserve Muscle During Weight Loss?
Your muscles need protein to repair and stay strong, especially during a calorie deficit. If you cut calories without enough protein, your body may break down muscle for energy instead of burning fat.
Many experts suggest at least 1.0 to 1.2 grams per kilogram of body weight to maintain muscle. For a 175 pound person, that is about 80 to 96 grams per day.
Fill meals with quality protein foods such as chicken, strained yogurt, eggs, or lentils. This strategy helps you lose fat while protecting lean muscle, which keeps your metabolism from slowing.
Additional Health Benefits of a High-Protein Diet
Higher protein can also steady blood sugar, support bones, and improve workout recovery. These benefits matter for long term health, not just the number on the scale.
How Does Protein Improve Blood Sugar Control?
Protein slows the digestion of carbohydrates. Slower digestion reduces sharp spikes in blood sugar after meals, which supports steady energy and mood.
Mayo Clinic resources note that pairing protein with carbs can help control post-meal blood glucose. Combine lean protein with fiber rich foods such as legumes, vegetables, and whole grains for an even smoother response.
Can a High-Protein Diet Support Better Bone Health?
Protein supports the building and repair of bone tissue. People who eat enough protein, from both animal and plant sources, tend to show better bone mineral density in studies.
Dairy products like milk and yogurt provide calcium plus high quality protein. Lean proteins such as chicken, fish, and beans also support your skeleton and general health as you age.
How Does Protein Enhance Muscle Strength and Recovery?
After exercise, your body repairs muscle fibers. Protein supplies amino acids, the building blocks needed for that repair process, called muscle protein synthesis.
Adults need at least 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight daily, and active people often need more. Spreading protein across the day, about three to five eating moments, supports recovery and helps limit muscle loss during weight loss.
Protein rich snacks, such as whey protein, Greek yogurt, or edamame, can fill gaps between meals. They also help you meet daily needs during busy schedules.
How Much Protein Should You Eat for Weight Loss?
Your ideal protein intake depends on body size, activity level, and goals. A clear target makes planning easier and reduces guesswork at mealtime.
What Are the Daily Protein Requirements?
The RDA sets a minimum of 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight for adults. For someone who weighs 175 pounds, about 79 kilograms, that equals about 63 grams per day.
For weight loss, many people do better at 1.0 to 1.2 g/kg, or roughly 80 to 96 grams per day for a 175 pound person. Some aim higher based on training and appetite control.
The National Academy of Medicine suggests that protein can range from 10% to 35% of daily calories. During weight loss, 20% to 30% is a practical starting point. Ask your clinician before making major changes to high protein diets.
How Should Protein Intake Be Adjusted Based on Activity and Goals?
If you exercise often or need to maintain muscle while you lose weight, increase protein intake. Many active adults choose 1.6 to 2.2 g/kg per day for fat loss while protecting muscle.
Use a mix of lean poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, beans, lentils, nuts, and seeds. Spread protein across four to five meals or snacks for better appetite control and recovery.
Older adults and pregnant people have unique needs, so speak with a healthcare professional. Anyone with kidney concerns should review protein goals with a clinician because too much can stress kidney function over time.
Best High-Protein Foods to Include in Your Diet
Mix animal and plant protein sources to hit your targets and meet vitamin and mineral needs. Variety also keeps meals interesting while you lose weight.
Why Choose Lean Meats Like Chicken, Turkey, and Fish?
Lean meats provide a lot of protein with less saturated fat. A 3 ounce serving of skinless chicken breast offers about 26 grams of protein and very little saturated fat.
Fish fillets provide about 17 to 20 grams of protein per 3 ounces. Salmon also delivers omega 3 fats that support heart health.
Choosing these options supports weight loss by boosting fullness without many extra calories from fat. Replacing fatty red meat with grilled chicken or baked fish can also help manage LDL cholesterol.
What Are the Benefits of Eggs and Dairy Products?
Eggs are a complete protein, which means they contain all essential amino acids. One large egg has about 6 grams of protein and cooks quickly.
Low fat dairy like yogurt and cottage cheese add protein plus calcium for bone health. Four ounces of low fat plain yogurt has about 6 grams of protein. A half cup of low fat cottage cheese provides about 12 grams. One ounce of provolone has roughly 7 grams.
Which Plant-Based Proteins Are Good Sources?
Plant proteins can cover a large share of daily needs. A 3 ounce serving of firm tofu provides about 9 grams of protein. A half cup of cooked lentils also gives about 9 grams. A half cup of kidney beans delivers about 8 grams.
Four ounces of soy milk has about 3 to 4 grams. Legumes such as chickpeas and lima beans supply protein and fiber, which support fullness and heart health. Soy foods like tofu and tempeh may also help lower LDL cholesterol.
Nuts, seeds, quinoa, pea protein powder, and peanut butter contribute protein along with useful micronutrients. Rotating these foods helps you meet your grams of protein per day without heavy reliance on processed meat.
Reference: Meta analysis on soy protein and lipoproteins reports cholesterol benefits in many studies.
How Do Nuts, Seeds, and Grains Contribute Protein?
Nuts, seeds, and whole grains add plant protein plus healthy fats and fiber. Two tablespoons of peanut butter provide about 7 grams of protein. Almond butter offers about 7 grams as well.
An ounce of almonds has around 6 grams. Pistachios provide similar amounts and work well in snack mixes. Pumpkin and chia seeds add protein and minerals such as magnesium.
Quinoa is a complete grain protein. Other whole grains like teff and kamut add moderate protein and fiber. Adding chickpeas or lentils to soups and salads increases staying power at lunch or dinner.
High-Protein Meal Plan to Support Weight Loss
A simple meal plan helps you hit protein goals, limit hunger, and protect muscle. Keep portions consistent and use repeatable meals on busy days.
What Is a Healthy High-Protein Breakfast?
Start the day with protein to steady appetite. Try two eggs with sautéed spinach and a slice of whole grain toast with avocado.
Greek yogurt with berries and a small amount of granola offers protein and fiber. If you prefer plant based options, cook oatmeal in soy milk for extra protein and top with almonds.
A half cup of cottage cheese gives about 12 grams of protein. Pair it with fruit or nuts. A simple smoothie made with low fat milk or soy milk is a quick option. Many people also use a protein shake on mornings with little time.
What Is a Balanced High-Protein Lunch?
Keep energy up with a lean protein base. Three ounces of skinless chicken breast provide about 26 grams of protein with little saturated fat.
Build a salad with greens, cucumbers, and a chopped hard boiled egg. Add beans or lentils for more fiber and protein. A half cup of cooked lentils adds about 9 grams and works in grain bowls or wraps.
For a plant based plate, add tofu to a bowl with quinoa and vegetables. A side of low fat Greek yogurt can supply extra protein and calcium.
What Makes a Good High-Protein Dinner?
Choose a lean protein, add vegetables, then include a whole grain or starchy vegetable. A 3 ounce salmon fillet delivers about 17 to 20 grams of protein and omega 3 fats.
Lean cuts of beef, like loin or round, can fit if you limit saturated fat and portion size. Vegetarian dinner ideas include tofu, tempeh, or a hearty bean chili.
Pair grilled fish with quinoa and roasted asparagus for a balanced meal. Use low fat dairy in recipes when possible and avoid fatty meats to protect blood pressure and heart health.
What Are Smart High-Protein Snack Options?
Greek yogurt with berries gives about 10 to 20 grams per serving, depending on size. Trail mix with nuts and seeds adds healthy fats and a few grams of protein.
An ounce of almonds has about 6 grams. Peanut or almond butter provides about 7 grams in two tablespoons. Spread it on apple slices or whole grain crackers.
Hard boiled eggs deliver about 6 grams each. Low fat cottage cheese offers around 12 grams in a half cup. Protein shakes are useful right after workouts when recovery is a priority. Roasted chickpeas or edamame make crunchy, plant based snacks that help you stay full between meals.
Tips for Following a High-Protein Diet Successfully
A few simple habits make higher protein eating easier to stick with. Plan ahead, hydrate well, and keep variety in your protein choices.
How Can You Combine Protein Sources for Complete Amino Acids?
Pair plant proteins to cover all essential amino acids. Beans or lentils with rice is a classic example and works in bowls, soups, and burritos.
Soy foods like tofu and tempeh are complete proteins on their own. Quinoa is another single plant food that covers the full set of amino acids.
You can also combine animal and plant proteins across the day. Add nuts and seeds to legume dishes for a stronger amino acid profile and better texture.
Why Is Staying Hydrated Important for Protein Digestion?
Water helps your body process the byproducts of protein digestion and supports kidney function. Higher protein intake increases the waste your kidneys need to filter, so extra fluids are helpful.
Drink more water if you add protein shakes or more meat and dairy. Good hydration also helps relieve constipation and dry mouth that some people notice with higher protein eating.
Protein can raise uric acid in some people, so steady fluid intake supports healthy clearance.
How Should You Balance Protein with Fiber, Fats, and Carbs?
Balance matters. Aim for protein at 20% to 30% of daily calories during weight loss. Carbohydrates can be 45% to 65%, and fats about 25% to 35%.
Choose higher fiber carbs like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and beans. Pick healthy fats from nuts, seeds, olive oil, fish, and avocados.
Divide calories across four or five eating moments to manage hunger and energy. Focus on nutrient dense foods instead of relying only on protein supplements.
Which Processed Protein Sources Should You Avoid?
Limit processed meats such as bacon, sausage, hot dogs, and deli slices. They are often high in saturated fat and sodium, which can raise LDL cholesterol and heart disease risk.
Watch commercial protein bars and shakes with added sugars or long ingredient lists. Choose simple foods, lean meats, fish, eggs, legumes, nuts, and low fat dairy most of the time.
Potential Risks of a High-Protein Diet
Higher protein is safe for most healthy adults, yet there are risks if you choose poor sources or have certain conditions. Know the red flags before you start.
How Can a High-Protein Diet Lead to Excess Saturated Fat?
Choosing fatty cuts of red meat or full fat dairy can push saturated fat too high. That pattern can raise LDL cholesterol and increase heart disease risk.
Pick lean cuts of beef or pork, or go with chicken, turkey, and fish more often. Use low fat or fat free dairy to keep saturated fat in check.
What Are the Kidney Risks of Too Much Protein?
High protein diets increase the amount of waste your kidneys must filter. If you have chronic kidney disease, this extra load may worsen kidney function.
People with diabetes or high blood pressure should be careful because these conditions already stress the kidneys. A clinician can help you set a safe range.
If you have any sign of kidney problems, do not raise protein without medical advice. The Journal of the American Society of Nephrology has reported faster kidney decline with high protein intake in people who already have chronic kidney disease.
How Can Cutting Carbs Cause Nutritional Imbalances?
Cutting carbs too far can lower your intake of fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Fruits, legumes, and whole grains provide nutrients that support digestion and heart health.
Very low carb patterns may cause headaches, fatigue, bad breath, or constipation. Keep a mix of protein, healthy fats, and smart carbs to meet your needs while losing weight.
Who Should Avoid a High-Protein Diet?
Some people need closer guidance or a different approach. If you have organ issues or a complex medical history, you need a personalized plan.
Why Should People with Kidney or Liver Issues Avoid High Protein?
If you have kidney or liver disease, your body may struggle with extra protein. Kidneys filter waste from protein metabolism. A damaged liver has trouble breaking down amino acids.
Too much protein in these situations can lead to a buildup of waste products, which can make you feel ill. People with diabetes or high blood pressure should also review protein goals with a healthcare provider.
Protein is essential, but dosing needs to match your health status. Work with your care team before raising protein intake.
Which Health Conditions Make High-Protein Diets Unsafe?
Chronic kidney disease limits how much protein you can process safely. Liver disorders can also worsen with excess protein.
Pregnancy and athletic training often need higher protein, but the exact amount should be set with a clinician or dietitian. Medications can change requirements too. Always get guidance before large diet changes.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Professional advice keeps your plan safe, efficient, and sustainable. A short visit now can prevent setbacks later.
Why Is Personalized Guidance Important for Protein Intake?
Experts can set a precise target for grams of protein per day, often 1.6 to 2.2 g/kg during weight loss. They also consider kidney health, training, age, and other factors.
A registered dietitian can design a meal plan that balances protein, fiber, fats, and carbs. Follow up visits let you adjust based on lab results, energy, and appetite.
How Should You Monitor Progress and Adjust Your Diet?
Track weight, waist, and simple strength markers weekly. Use a food diary or app to log meals and confirm you are hitting your protein goals.
Watch energy, sleep, and workout recovery. If progress slows, adjust portions of lean protein, add vegetables, or increase steps and resistance training. If you have medical conditions, make changes with your clinician or dietitian.
Consistent tracking shows what works, so your adjustments are based on data, not guesswork.
Conclusion
A high-protein diet can help you lose weight while protecting muscle and curbing hunger. Protein’s thermic effect, higher fullness, and role in muscle maintenance work together to support steady results.
Choose a variety of healthy protein sources and aim for 20% to 30% of calories from protein during weight loss. If you have kidney or liver issues, or you take certain medicines, talk with a healthcare professional first. Evidence from clinical research supports protein as one key part of successful weight management.
With clear protein targets and simple meals, you can move toward your goals and maintain progress with confidence.
[1] Leidy HJ, Clifton PM, et al., The Role of Protein in Weight Loss and Maintenance, Am J Clin Nutr 2015;101(6):1320S-1329S
FAQs
1. Why is protein an important part of a weight loss diet?
Protein is an important nutrient for overall health and supports muscle maintenance during weight loss. Studies show that higher protein intake helps people feel full longer, which can reduce calorie intake and support fat loss.
2. How does protein affect amino acid levels in the body?
Protein provides essential amino acids that the body cannot make on its own. These amino acids help repair tissues, build muscle, and maintain healthy metabolism while losing weight.
3. What evidence links high-protein diets to successful weight management?
Research shows that increased dietary protein was associated with greater fat loss compared to lower-protein diets. One study found participants eating more protein lost more body fat while keeping lean mass intact (Leidy et al., 2015).
4. Does eating more protein also benefit other aspects of health beyond weight control?
Yes, research suggests that higher dietary protein also improves blood sugar control and supports heart health when combined with balanced nutrition (Westerterp-Plantenga et al., 2009). Protein also helps preserve bone density as part of a healthy lifestyle.
Summary: A high-protein diet offers benefits for overall health by supporting muscle retention, providing key amino acids, aiding in appetite control, and helping manage blood sugar levels during weight loss efforts.







